Math Equation Used
Simple Interest Formula:
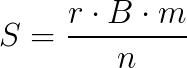
where
S = simple interest
r = simple annual interest rate
B = P = initial balance or principal
m = number of time periods elapsed and
n = frequency of applying interest
Example: Imagine that a credit card holder has an outstanding balance of $2500 and that the simple annual interest rate is 12.99% per annum,
applied monthly, so the frequency of applying interest is 12 per year.
Over one month,
(0.1299 x $2500 x 1mo) / 12 = $27.06
interest is due (rounded to the nearest cent).
Simple interest applied over 3 months would be
(0.1299 x $2500 x 3mo) / 12 = $81.19
If the card holder pays off only interest at the end of each of the 3 months, the total amount of interest paid would be
[(0.1299 x $2500) / 12] x 3 = $27.06 per month x 3 months = $81.18
which is the simple interest applied over 3 months, as calculated above. (The one cent difference arises due to rounding to the nearest cent.)
Simple Interest Formula variation:
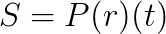
where
S = simple interest
P = B = principal or initial balance
r = rate
t = time
This formula is used to calculate money earned/paid that does not have compounding.
No money is earned from the interest that was earned in prior years.
Note: As with any financial formula, it is important that rate and time are appropriately measured in relation to one another.
If the time is in months, then the rate would have to be the montly rate and not the annual rate.
References
Interest. (2019, February 25). Retrieved from
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interest